Ultimate Bearing Replacement Guide
 The Bearing Search, Simplified: Quick & Affordable Replacements
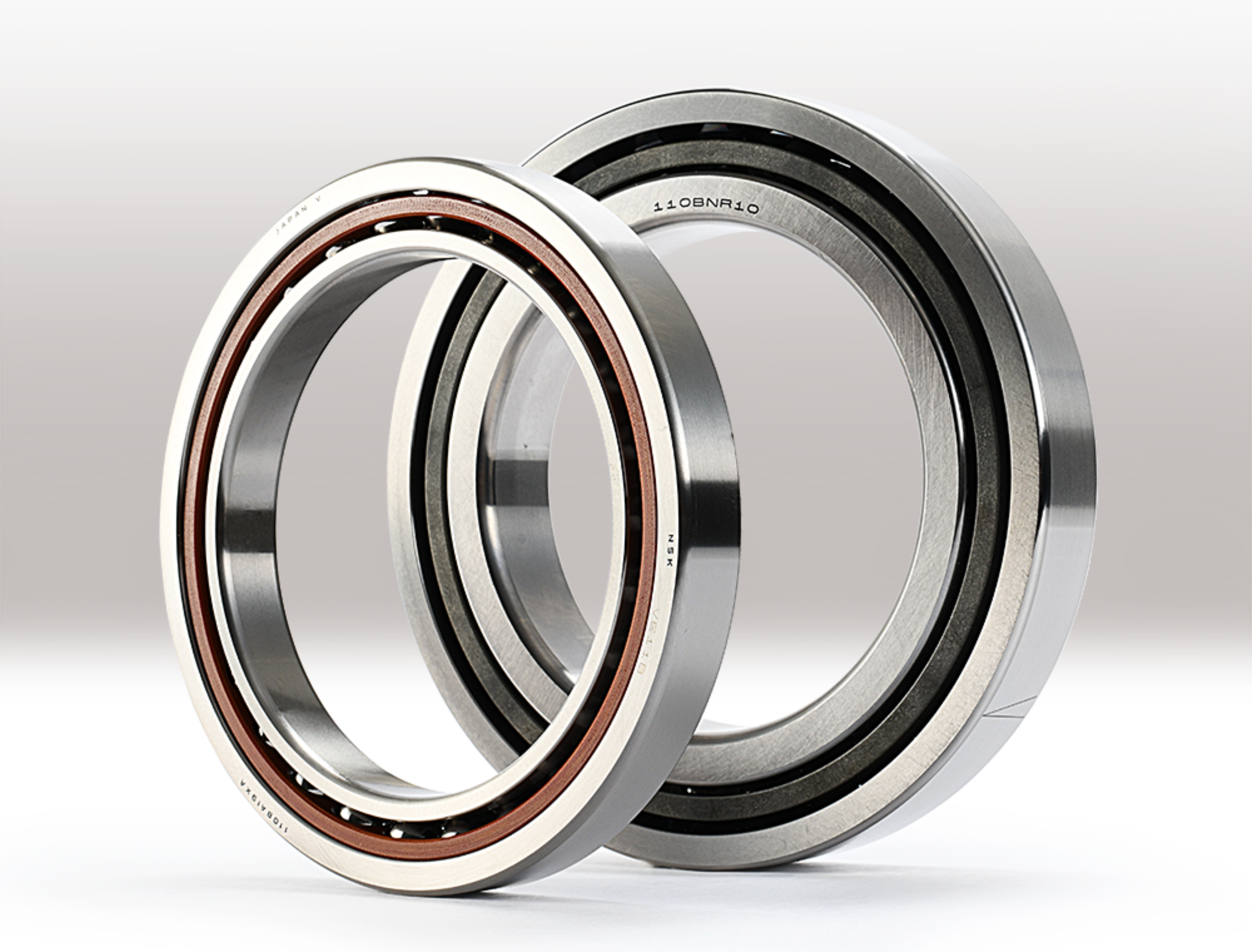
The Bearing Search, Simplified: Quick & Affordable Replacements
Bearings are critical components that support and guide rotating shafts while reducing friction between moving parts. By using rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, placed between inner and outer raceways, bearings allow machinery to rotate smoothly and efficiently with minimal resistance.
Selecting the right bearing is essential for machine tool accuracy and reliability. Different types serve different purposes—angular contact bearings ensure precision, while thrust bearings are designed to handle axial loads. For example, most motorized spindles in machine tools include at least two sets of ball and cylindrical roller bearings, which directly affect the spindle's lifespan and overall performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Bearings
Finding the ideal bearing for your application requires careful consideration of key factors, including:
- Load Capacity: Ensure the bearing can handle the weight and forces it will be subjected to.
- Speed: Choose a bearing compatible with the operational speed of the machinery.
- Rigidity: The bearing must provide the necessary stiffness for precise operation.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is critical for reducing wear and extending lifespan.
- Environment: Assess conditions like temperature, moisture, and dust exposure.
- Noise Levels: Particularly important for applications where quiet operation is required.
All World’s customer service team has decades of experience in helping customers find the correct bearings for their specific needs. Whether you're performing routine maintenance or replacing a worn-out component, we make the process easy.
 Cross-Referencing Bearings with Confidence
Cross-Referencing Bearings with ConfidenceWe specialize in cross-referencing bearings to replace original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. By providing key specifications—such as inner and outer diameter, configuration, and part number components—our experts can quickly identify a high-quality replacement. Even if it’s a different brand, such as Timken or NSK, these bearings are designed to deliver the same performance as your original—or even better.
Even with limited part numbers, we can determine the proper substitute by leveraging details like:
- Inner and Outer Diameter
- Configuration and Design
- Bearing Number Components (Prefix, Basic Designation, and Suffix)
The basic designation of a bearing number holds valuable information about its type and specifications. For instance, the first digit signifies the series' width or height, while the last two digits indicate the size code for the bearing bore. By understanding these elements, interpreting bearing numbers becomes much simpler.
For angular contact bearings, the first two digits point to the brand and the number of rows. The third and fourth digits specify the series, while digits five through nine detail the bearing material. Additional digits provide insights into the radial clearance and precision rating.
If you only have a partial bearing number, don’t worry—just send us a picture. Include the inner and outer diameter measurements along with the image, and we’ll identify the correct replacement for you. Often, we can identify the bearing and ship it on the same day.
During the crossing process, we can also determine your spindle’s configuration, such as back-to-back (DB), face-to-face (DF), tandem (DT), triplex (DBB), or quad (DBBT). Identifying the configuration ensures you have the correct options in your inventory, minimizing downtime when replacements are needed.
Additionally, we offer a wide selection of duplex bearings and single universal flush grinds. Using universal options can simplify inventory management by reducing the number of specialized bearings you need to keep on hand.
Precision Matters
The final two digits of an angular contact bearing indicate its precision level. The letter "P" represents precision, followed by a number that specifies the accuracy level—a higher number indicates greater precision. For example, under the ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) standard, P4 corresponds roughly to ABEC 7, while P5 aligns with ABEC 5.
P4 and P5 bearings are ideal for high-precision applications requiring smooth and accurate rotation. These include high-end machine tools, precision instruments, and high-speed motors. They are also critical in scenarios where even minimal variations in bearing dimensions could significantly affect performance.
At All World, we primarily offer P4 bearings, which deliver exceptional precision at a highly competitive price.
Ensuring Proper Lubrication
Most All World bearings are designed with an oil slot, making them compatible with automatic lubrication systems. If you do manual greasing, don’t worry—the hole is small enough to prevent grease from leaking out of the bearing.
At All World, we stock Kluber NBU-15, a premium grease perfect for high-heat and high-speed applications. Not sure how much grease to use? We can calculate the exact amount based on your specific bearing and application. We’ll also recommend the right amount of grease to ensure proper application to the cavities.

Main Categories of Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings feature offset inner and outer ring raceways along the bearing axis, enabling them to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously. Commonly used as spindle bearings, they are perfect for high-speed, precision applications.
Ball Thrust Bearings
Thrust ball bearings are compact, cost-effective components designed for low speeds and light to medium loads. Common in car transmissions, pumps, compressors, and fans, they ensure smooth operation by handling axial pressure in one direction.
Linear Bearings
Linear bearings enable smooth, straight-line motion by using trucks and rails—where the rail remains stationary and the truck slides with the help of small balls or rollers to reduce friction. Essential in machines like CNC tools, industrial robots, 3D printers, conveyor belts, and packaging systems, they enhance precision, reliability, and efficiency.
Needle Bearings
Needle bearings, also known as needle roller bearings, are compact, lightweight cylindrical rollers that minimize friction in moving parts. Their slim design makes them perfect for high-speed, lightweight machinery and they're commonly found in gearboxes, automotive parts, aerospace devices, and machine tools.
Radial & Deep Groove
Radial or deep groove ball bearings consist of an inner ring, outer ring, cage, and small steel balls. Their unique "deep groove" design handles forces from multiple directions, making them ideal for stabilizing rotating shafts under radial forces. Commonly used in electric motors, they ensure smooth and reliable shaft rotation.
Roller Thrust Bearings
A roller thrust bearing uses cylindrical rollers to handle axial loads rather than radial loads. It ensures smooth rotation while supporting significant thrust in one direction. Commonly used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and pumps, these bearings are ideal for medium to large axial loads, providing high load capacity and rigidity, especially in compact spaces.
Spherical Bearings
A spherical bearing is a type of bearing that helps parts rotate while also handling misalignment between shafts. It's commonly used in heavy machinery, gearboxes, and other equipment where shafts might not line up perfectly due to load changes. It ensures smooth rotation even when things aren’t perfectly aligned.
All World has thousands of bearings in stock which are available for same-day shipment. For help finding the right one, right away, contact us today.



